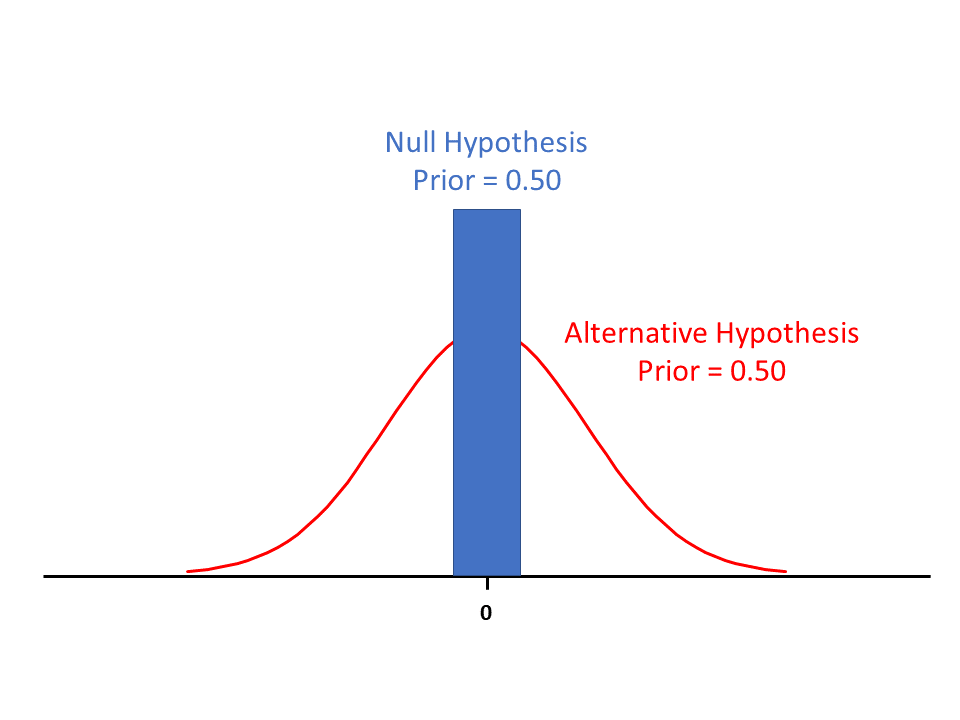
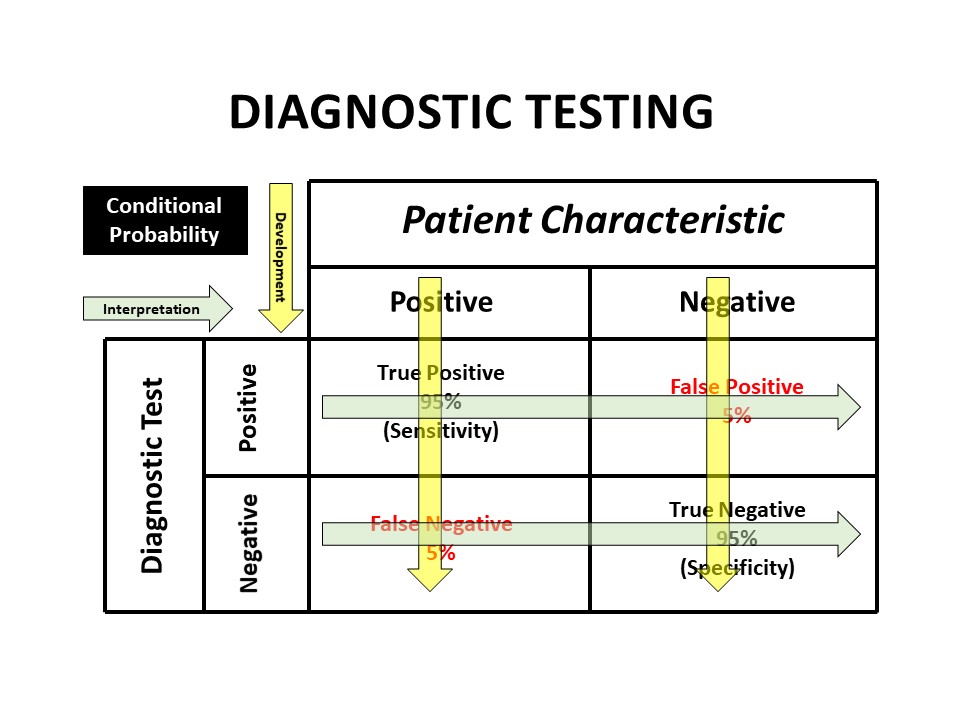
Bayesian and frequentist approaches to inference or prediction are very different. How different? This simple example highlights the difference and the argument in favor of using Bayesian posterior probabilities.
Tag: Bayesian statistics
No. 13: Unconsciously Biased and Consciously Unbiased
Implicit models in the back of our minds can creep into explicit models creating biased predictions that have societal implications.
No. 12: Models – Implicit and Explicit
If we fail to acknowledge that we have biases and assumptions that influence our assessment of 'objective facts,' then we delude ourselves. Our perception of reality and how we judge evidence is colored by our beliefs which arise from our specific experiences.
No. 11: Some Beliefs in Priors
The probability that the null hypothesis is true is 0.50. How should we interpret that and then write it down mathematically?
No. 9: Case Study – Genetic Subgroups and CV Disease
The over-reliance on p-values can lead to misinterpretation of data and a $150 million bet on a subgroup with scant evidence.
No. 8: Let’s Get Real – Bayes and Biomarkers
How do we know when an observed effect is real or spurious?
No. 6: Détente – The Peaceful Co-Existence of Significance Levels and Bayes
pr(B|A) ≠ 1 – pr(A|B). Why do we act like it ?!